Before packing, check this list of items prohibited from entering a particular country or region.
Unfortunately, some shipments are being rerouted due to international tensions in the Red Sea, causing delays. Please read our blog article for more information.
Best health systems in the world: which country would you pick?
Access to quality healthcare varies significantly between countries. From universal coverage to cutting-edge technology, we explore the nations leading the way in healthcare delivery so you can choose the best country to live in.
In this guide, we'll discuss which countries have the best healthcare systems and who offers free health services to their residents. We explain the European Health Insurance Card and the Global Health Insurance Card, both valuable resources for healthcare access while travelling. Plus, the difference between the healthcare systems of the United Kingdom and the United States, and more.
In countries with free-at-the-point-of-entry healthcare, such as the United Kingdom and Canada, it's considered a fundamental human right, regardless of financial status.
How are health systems different in other countries?
Worldwide healthcare systems differ in structure, availability of funds and accessibility for citizens. In countries with free-at-the-point-of-entry healthcare, such as Canada's Medicare and the United Kingdom's NHS, it's considered a fundamental human right, regardless of financial status.
Such systems are funded by taxation, providing access to essential medical services for all, including doctor visits, hospital stays and operations. Similar systems exist in many other countries, including Sweden, Norway, New Zealand and Australia.
In contrast, countries like the United States focus on private healthcare, where access depends on an individual's insurance coverage. However, those on lower incomes, pregnant women and children can access the government-subsidised Medicaid.
Germany, Switzerland, and others utilise a mix of public and private insurance, offering universal coverage via competing insurance companies, which are mainly accessed through employers.

Facts about healthcare around the world

Healthcare rankings by country
The best healthcare in the world is supplied by the Taiwanese healthcare system according to the 2023 edition of the CEOWORLD magazine Health Care Index. The index evaluated 110 countries, awarding each a score out of a hundred based on factors like medical infrastructure, healthcare staff's abilities and qualifications, and the cost and availability of medicines. Further considerations include environmental care, access to clean water, sanitation, and government actions to address tobacco use and obesity.
Two additional Asian nations made the top ten, with South Korea claiming second place and Israel in tenth. Europe also performed well, making up an impressive five of the top ten spots: Sweden in 5th place, Ireland in 6th, the Netherlands in 7th, Germany in 8th, and Norway in 9th.
| Rank | Country | Infra-structure | Availability and cost | Overall index |
| 1 | Taiwan | 87.16 | 83.59 | 78.72 |
| 2 | South Korea | 79.05 | 78.39 | 77.7 |
| 3 | Australia | 90.75 | 82.59 | 74.11 |
| 4 | Canada | 86.18 | 78.99 | 71.32 |
| 5 | Sweden | 78.77 | 74.88 | 70.73 |
| 6 | Ireland | 92.58 | 96.22 | 67.99 |
| 7 | Netherlands | 77.86 | 71.82 | 65.38 |
| 8 | Germany | 86.28 | 75.81 | 64.66 |
| 9 | Norway | 72.48 | 68.68 | 64.63 |
| 10 | Israel | 88.63 | 75.61 | 61.73 |
What country has the best healthcare?
The Health Care Index has named Taiwan as the country with the best healthcare due to its short waiting times and low cost. However, while moving to Taiwan might now be at the top of your agenda, the question of which country has the "best" healthcare is still open to debate as many other worldwide healthcare systems excel in different areas.
Switzerland consistently scores high in healthcare performance. All Swiss citizens and residents must have basic health insurance provided by private insurance companies. It covers various medical services, including hospital stays, doctor visits and prescriptions. The Swiss government regulates insurers to guarantee high standards.
Singapore's healthcare system is also widely praised for its universal coverage, affordability and efficiency. The government prioritises preventive care and strongly encourages citizens to save for healthcare expenses, resulting in one of the world's longest life expectancies of 84.8 years.
Other high-performing countries include Germany, which has innovative and affordable medication, and the Netherlands, which emphasises patient-centred care.

List of countries with free healthcare
The following is a partial list of countries with free or universal healthcare systems:
- Australia
- Austria
- Belgium
- Botswana
- Brazil
- Brunei
- Canada
- China
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Denmark
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Hong Kong
- Iceland
- Italy
- Japan
- Luxembourg
- Macau
- Malaysia
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Norway
- Portugal
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Thailand
- Turkey
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom

What countries have free healthcare?
Many countries worldwide offer free or heavily subsidised healthcare. One popular system is the concept of universal healthcare, where access to medical services is considered a basic right regardless of how much money a person possesses. Such systems are in place in the United Kingdom, Australia, and Canada and are funded by taxation. Similar systems in countries like Japan and South Korea offer primary healthcare via mandatory, government-run health insurance programs. In both cases, some services, such as vision care, dental care and prescriptions, may be excluded.
Some countries, particularly in Africa and Asia, run community-based health insurance systems. Communities pool resources and funds to provide local healthcare coverage. It's more common in low-income countries with vast rural areas where formal health insurance is often limited.
What is the country with the highest life expectancy?
Monaco had the world's highest life expectancy.
For men:
84 years old
For women:
89 years old
Source: Statista
The EHIC covers emergency treatment, maternity care, treatment for pre-existing conditions and more.
The European Health Insurance Card: what is it and how to apply
The European Health Insurance Card (EHIC) is a free scheme for citizens of the European Union (EU), the European Economic Area (EEA), and Switzerland. It grants access to essential healthcare services without excessive costs during short stays in all participating countries.
The EHIC covers emergency treatment, maternity care, treatment for pre-existing conditions and more. It mainly benefits holidaymakers, international students, and expats working in other EU or EEA countries.
You can apply for an EHIC via your home country's national healthcare system, usually through the official website. You must provide personal details like your name, address and national insurance number. Once approved, your card is valid for up to five years.
The EHIC shouldn't be substituted for travel insurance, as it may not cover all medical costs or other travel-related emergencies, such as delayed flights home.
What is a Global Health Insurance Card?
The UK introduced the Global Health Insurance Card (GHIC) in 2021, replacing the European Health Insurance Card (EHIC). Like the EHIC, the GHIC provides access to necessary healthcare services during short stays in European Union (EU) countries, including Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
The GHIC lets UK residents receive healthcare, including treatment for pre-existing conditions, at the same cost as citizens of the country they are visiting.
UK residents can apply online via the National Health Service (NHS) website. The card is free of charge and valid for up to five years. You must provide the National Insurance numbers of all the family members over 16 you're applying on behalf of. Depending on your medical history, you may also need your NHS number.
The GHIC replaces the EHIC for UK residents. However, you can still use your EHIC until it expires. Like the EHIC, the GHIC is not a replacement for travel insurance, so it's advisable to ensure you are fully covered before departure.

UK vs US healthcare
While the UK and the USA have much in common, including a shared language and similar democratic governments and cultures, their healthcare systems starkly contrast regarding structure, access, and financing.
The National Health Service (NHS), a publicly-funded body, provides healthcare to all UK residents. Most medical services, including doctor visits, hospital care, and surgeries, are free at the point of use and funded primarily by taxation. The purpose of the NHS is to provide comprehensive care to all, regardless of their ability to pay. Private, self-funded healthcare is available for those who require specialised or quicker treatment through various health insurance providers.
Conversely, the US healthcare system is mainly privatised with a mix of public and private insurance providers — an essential consideration when moving to the USA. Healthcare is commonly purchased via employers or private insurance plans, which can be expensive, leading to differences in coverage for those without insurance. Medical services are often difficult to afford, even for insured individuals and families, thanks to out-of-pocket expenses like copays, deductibles and premiums.
Countries with the highest health care costs
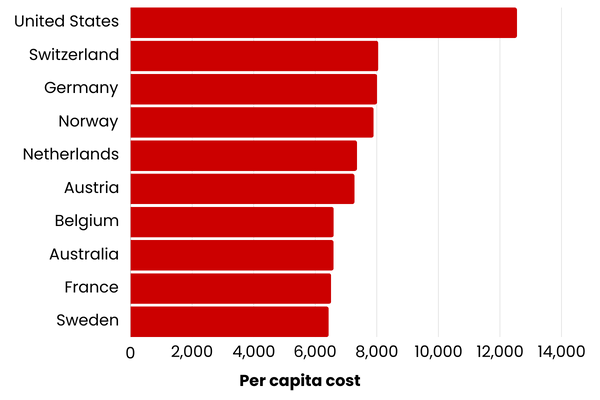
Source: World Population Review — health care costs by country









